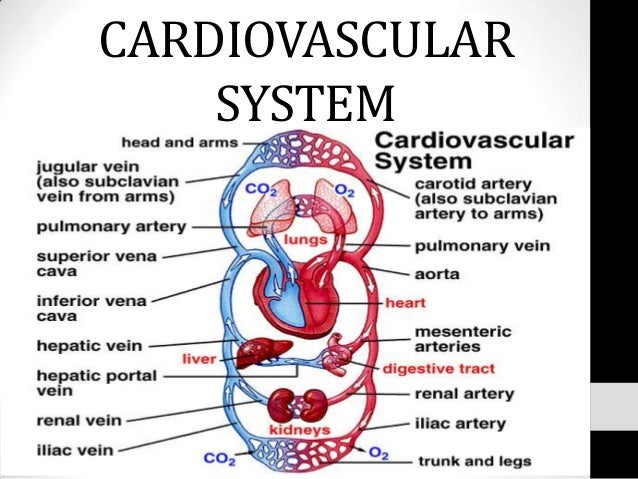
This system is made up of the heart, veins, capillaries, and arteries (blood vessels). The purpose of this system is to transfer oxygen, and nutrients to tissues, and then get the waste products to the organs that can properly dispose of them. Veins bring blood into the heart while arteries carry the blood from the heart around the whole body. The body’s total supply of blood is at around 5 liters. Which the heart is able to pump out every minute. There are two types of circulatory loops the pulmonary and systemic circulation loops. Blood vessels are lined with simple squamous epithelium which has this to stop clots, and keep blood inside. Inside the heart epithelium is called the endocardium. This system transports, maintains homeostasis, and protects. To regulate the blood vessels open up to spill out blood during times of heat, and when it is cold they constrict to keep blood flowing to the core. The blood vessels also help to make a buffer to keep the pH stable, and they create an isotonic environment for cells. The white blood cells serve to fight pathogens, and clean cellular waste, the red blood cells get with platelets to prevent blood loss, and cover open wound. Antibodies are stored in blood to protect from invaders, and hold immunity to previous pathogens.
Antibodies: a blood protein produced in response to and counteracting a specific antigen. Antibodies combine chemically with substances that the body recognizes as alien, such as bacteria, viruses, and foreign substances in the blood.
antigens: a toxin or other foreign substance that induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies.
Aorta: the main artery of the body, supplying oxygenated blood to the circulatory system. In humans it passes over the heart from the left ventricle and runs down in front of the backbone.
Arteriole: a small branch of an artery leading into capillaries.
artery: any of the muscular-walled tubes forming part of the circulation system by which blood (mainly that which has been oxygenated) is conveyed from the heart to all parts of the body.
Atrium: each of the two upper cavities of the heart from which blood is passed to the ventricles. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the veins of the body; the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary vein.
Capillary: any of the fine branching blood vessels that form a network between the arterioles and venules.
circulatory system: the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, blood, lymph, and the lymphatic vessels and glands.
diastole: the phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscle relaxes and allows the chambers to fill with blood.
ECG: a simple, noninvasive procedure.
Myocardium: the muscular tissue of the heart.
Pacemaker: an artificial device for stimulating the heart muscle and regulating its contractions.
peripheral resistance: near the surface of the body, with special reference to the circulation and nervous system.
Platelets: a small colorless disk-shaped cell fragment without a nucleus, found in large numbers in blood and involved in clotting.
pulmonary circulation: is the portion of the cardiovascular system which carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart, to the lungs, and returns oxygenated (oxygen-rich) blood back to the heart.
Purkinje fibers: carry the contraction impulse from both the left and right bundle branch to the myocardium of the ventricles.
red blood cells: typically a biconcave disc without a nucleus. Erythrocytes contain the pigment hemoglobin, which imparts the red color to blood, and transport oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from the tissues.
sinoatrial node: a small body of specialized muscle tissue in the wall of the right atrium of the heart that acts as a pacemaker by producing a contractile signal at regular intervals.
systemic circulation: part of the cardiovascular system which carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body, and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Systole: the phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscle contracts and pumps blood from the chambers into the arteries.
valves of the heart: any of the valves that control blood flow to and from the heart and that include the atrioventricular valves, the aortic valve, and the pulmonary valve—called also cardiac valve.
Vasoconstriction: the constriction of blood vessels, which increases blood pressure.
vasodilatation: the dilatation of blood vessels, which decreases blood pressure.
Vein: any of the tubes forming part of the blood circulation system of the body, carrying in most cases oxygen-depleted blood toward the heart.
vena cava: a large vein carrying deoxygenated blood into the heart.
Venule: a very small vein, especially one collecting blood from the capillaries.
Viscosity: the thickness and stickiness of blood.
white blood cells: a colorless cell that circulates in the blood and body fluids and is involved in counteracting foreign substances and disease; a white (blood) cell.
https://www.docsity.com/en/news/education-2/systems-human-body-interactive-gifs/
https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cardiovascularsystem-130721124922-phpapp01/95/cardiovascular-system-1-638.jpg?cb=1374411022
No comments:
Post a Comment